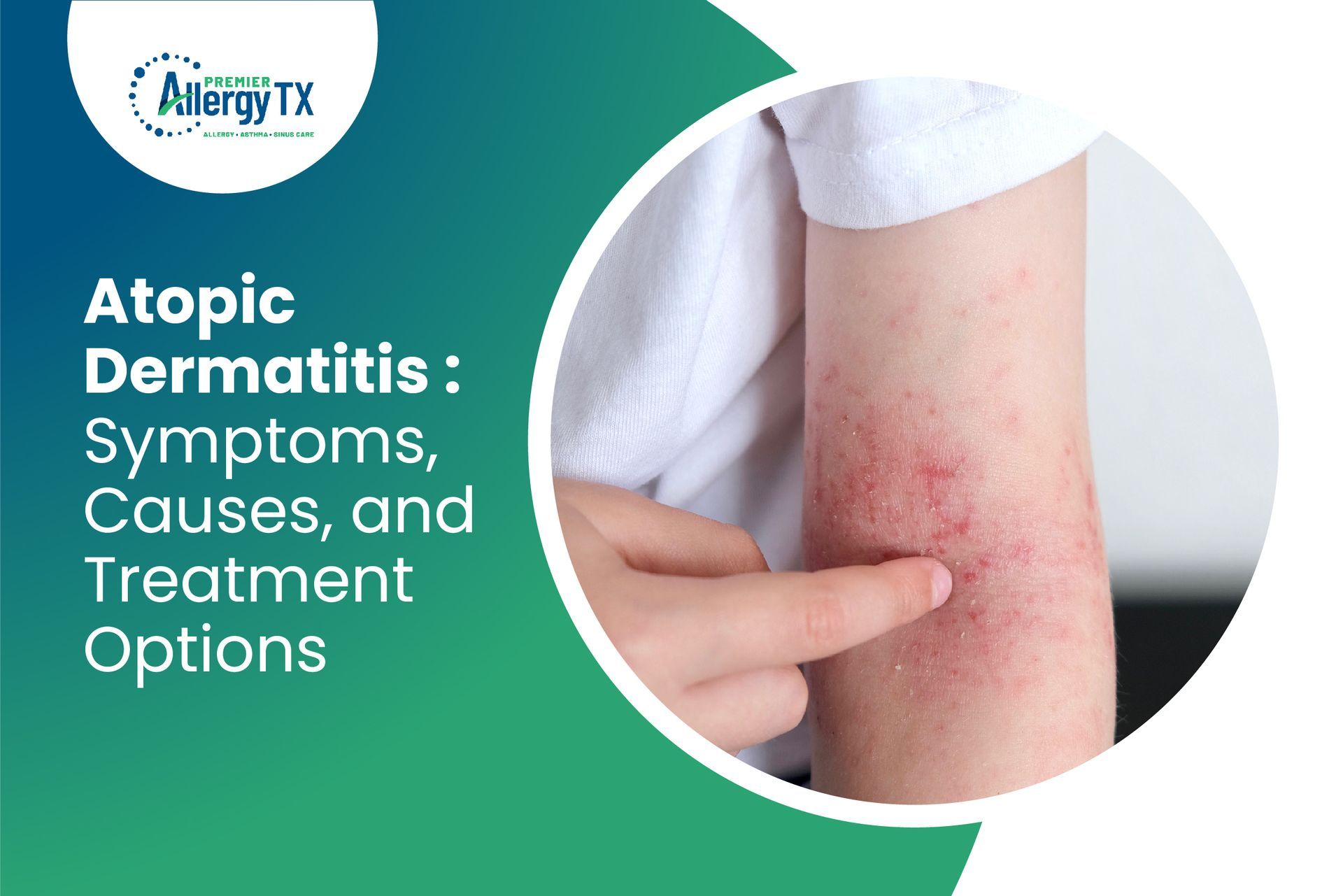
Tired of constant itching, red patches, and dry skin that just won’t go away? You might be one of the millions living with atopic dermatitis—a frustrating and often misunderstood skin condition. Whether you're newly diagnosed or searching for better ways to manage symptoms, this guide breaks it all down so you can finally get relief.
Atopic dermatitis
is an irritating, persistent skin disorder affecting millions worldwide. This disorder, commonly known as atopic eczema, is more common in children but can also affect adults. It is a complex disease with no cure, but several treatment options are available to manage
Atopic Dermatitis symptoms
and improve the quality of life of people with this condition.
Atopic Dermatitis Statistics
Recent studies have shed light on the prevalence of atopic dermatitis in the United States. According to these studies, approximately 7.3% of adults in the U.S. are affected by this
chronic skin condition. Of those individuals, about 40% experience moderate to severe symptoms, which can significantly impact their quality of life. These findings highlight the importance of proper diagnosis and treatment for atopic dermatitis, as early intervention can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Although atopic dermatitis is prevalent in people of color, little research has been conducted to determine the efficacy of Atopic Dermatitis (AD) treatments in these patients. Historically, studies on AD treatments have focused on white ethnic groups, with 62.1% of clinical trials published between 2000 and 2009 primarily including white patients. Only 10.3% of studies have considered
race or ethnicity when interpreting their results.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a skin disorder that causes dry, itchy, and irritated skin. The condition typically starts in childhood, with around 60% of cases
occurring in the first year of life and 90% before age 5. However, it can also occur in adults. The condition is often referred to as atopic eczema, one of the most common types.
Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms
Atopic dermatitis symptoms might differ from person to person, but the most common ones include:
- Dry skin
- Itching
- Red or
brownish-gray patches
on the skin
- When scraped, little raised lumps may leak fluid and crust over
- Skin that is thick, cracked, or scaly
- Raw,
sensitive, and swollen skin from scratching
These symptoms typically appear on the face, neck, hands, feet, and the inside bends of elbows and knees. In severe cases, the symptoms can affect the whole body.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Atopic Dermatitis Rash
Is Atopic Dermatitis Rash Contagious?
No, atopic dermatitis rash is
not contagious. It is a chronic skin condition caused by
genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. While the rash can appear unsightly, it is not caused by an infection and cannot spread from person to person.
What Does Atopic Dermatitis Rash Look Like?
Atopic dermatitis rash typically appears as dry, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. The rash can be red or brownish-gray, and it may have small raised bumps that can leak fluid and crust over when scratched. The rash can appear on different body parts, including the face, neck, hands, feet, and inside bends of elbows and knees.
Atopic Dermatitis Causes
Atopic dermatitis has no established etiology. However, it is thought to be caused by genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Researchers have found that people with atopic dermatitis have a gene mutation that affects the skin's ability to protect against moisture loss and harmful substances. This makes the skin dry, itchy, and prone to infection.
Environmental variables such as allergens, irritants, and stress can cause or exacerbate symptoms in persons with
atopic dermatitis.
Typical triggers include:
- Allergens
include dust mites, pollen, and pet dander.
- Irritants such as soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics
- Hot and cold temperatures, humidity, and sweat
- Stress and anxiety
- Irritations, such as cold sores, strep throat, and certain viruses
Atopic Dermatitis vs Eczema
The most prevalent eczema is atopic dermatitis, commonly used interchangeably with "eczema." It is essential to clarify, however, that not all varieties of eczema are atopic dermatitis, and the two names should not be used interchangeably. Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition characterized by an overactive immune system, and it is frequently connected with other allergy disorders, including
asthma and
hay fever. Different types of eczema, such as contact dermatitis , are caused by exposure to irritants or allergens and do not involve the immune system. Regardless of the type of eczema, the symptoms can be similar, and treatment options may overlap. However, proper diagnosis by a dermatologist or healthcare provider is essential to determine the most effective treatment plan.
How to Get Rid of Atopic Dermatitis?
There is currently no cure for atopic dermatitis, but several treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life of people with this condition. Treatment options include:
Applying
moisturizers
regularly can help prevent dryness and itching. Choose a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizer that is suitable for sensitive skin.
These medications are applied directly to the affected skin to reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
Topical corticosteroids are available in several strengths, and your doctor will determine which one is best for you.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
These medications can help relieve itching and reduce the need to scratch. They are available over the counter or by prescription.
These medications can help relieve itching and reduce the need to scratch. They are available over the counter or by prescription.
The skin is exposed to regulated levels of UV radiation during phototherapy. This can help reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
Phototherapy is typically used for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis that has not responded to other treatments.
The treatment of atopic dermatitis usually involves a combination of drugs, lifestyle adjustments, and avoidance of triggers. If you suspect that you have atopic dermatitis, you should consult with your doctor or a dermatologist. They will physically examine your skin and recommend the appropriate treatment options.
Cure for Atopic Dermatitis?
At present, there is
no cure for atopic dermatitis, but researchers are continually developing
new treatments and medications that may help manage the symptoms of this condition. Some of the latest
atopic dermatitis treatments being researched include biologic drugs targeting specific parts of the immune system and gene therapies aiming to correct the genetic mutations that cause atopic dermatitis.
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis: Insights into Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatment Options
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Although the precise cause of atopic dermatitis is unknown, it is thought to be related to an overactive immune system and genetic factors. Symptoms of atopic dermatitis can be managed through various treatment options, including topical medications, lifestyle changes, and phototherapy.
Do you suffer from the discomfort and irritation of
atopic dermatitis rash? Premier Allergy TX can help. Our team of experienced allergists and healthcare professionals specializes in treating skin allergies, including atopic dermatitis. We can create customized treatment regimens to assist you in controlling your symptoms and improving your quality of life. Don't let atopic dermatitis control your life. Take the first step towards relief by calling us at (210) 791-7856 or visiting Premier Allergy TX
to
schedule a consultation and learn how we can help you get back to healthy, clear skin.